NCEA compared with School C and Bursary

How is NCEA different from School Certificate and Bursary qualifications?
What's on this page?
What were School Certificate and Bursary?
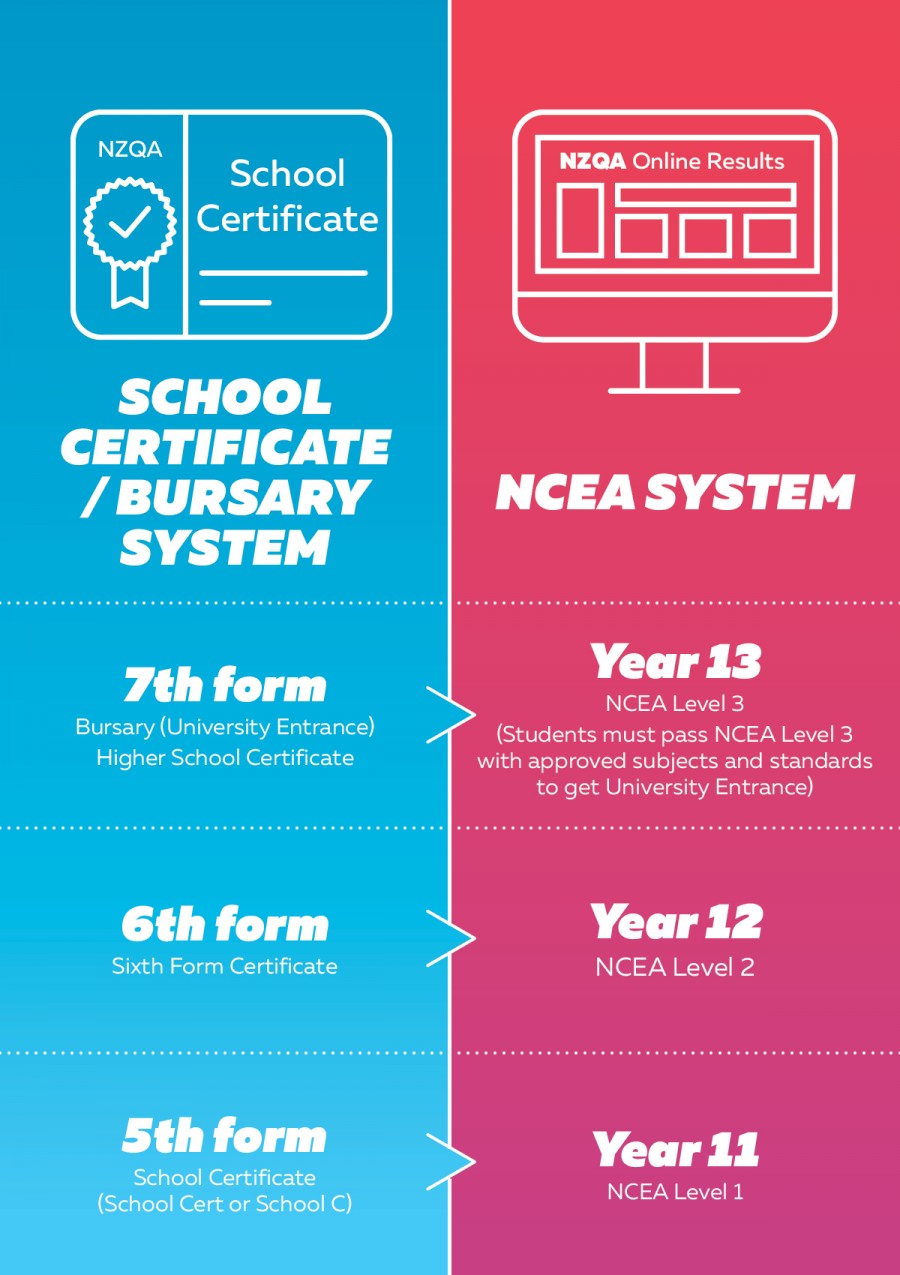
School Certificate (School Cert or School C) and Bursary were qualifications New Zealand secondary school students studied before 2002. Students studied five or six subjects a year, then usually had one chance a year to pass each subject by sitting a three-hour exam in November. Some subjects such as art, woodwork and physical education had internal assessment.
- Students in fifth form (Year 11) did School Certificate.
- Sixth form (Year 12) subjects were internally assessed and students gained Sixth Form Certificate. Students could also study University Entrance subjects.
- Students in seventh form (Year 13) did Bursary exams for University Entrance.
What is NCEA?
The National Certificate in Educational Achievement (NCEA) was introduced in 2002. The main change is students can achieve standards within subjects throughout the year rather than pass a subject by sitting one exam. Standards are worth credits, and students can achieve enough credits to be awarded NCEA Level 1, 2 or 3, which are studied in Year 11, Year 12 and Year 13.
Why was NCEA introduced?
Under the old system, students’ results were often scaled so that only a certain number of students could pass. This meant some students would receive a fail grade regardless of how well they performed.
NCEA measures each student’s learning against set standards, instead of comparing students and ranking them. Not all skills and knowledge can be assessed using tests and exams, for example, fluency in foreign languages, and competency in conducting science experiments.
NCEA provides a range of assessment methods that are appropriate to the subject being assessed.
NCEA graded differently from School C and Bursary
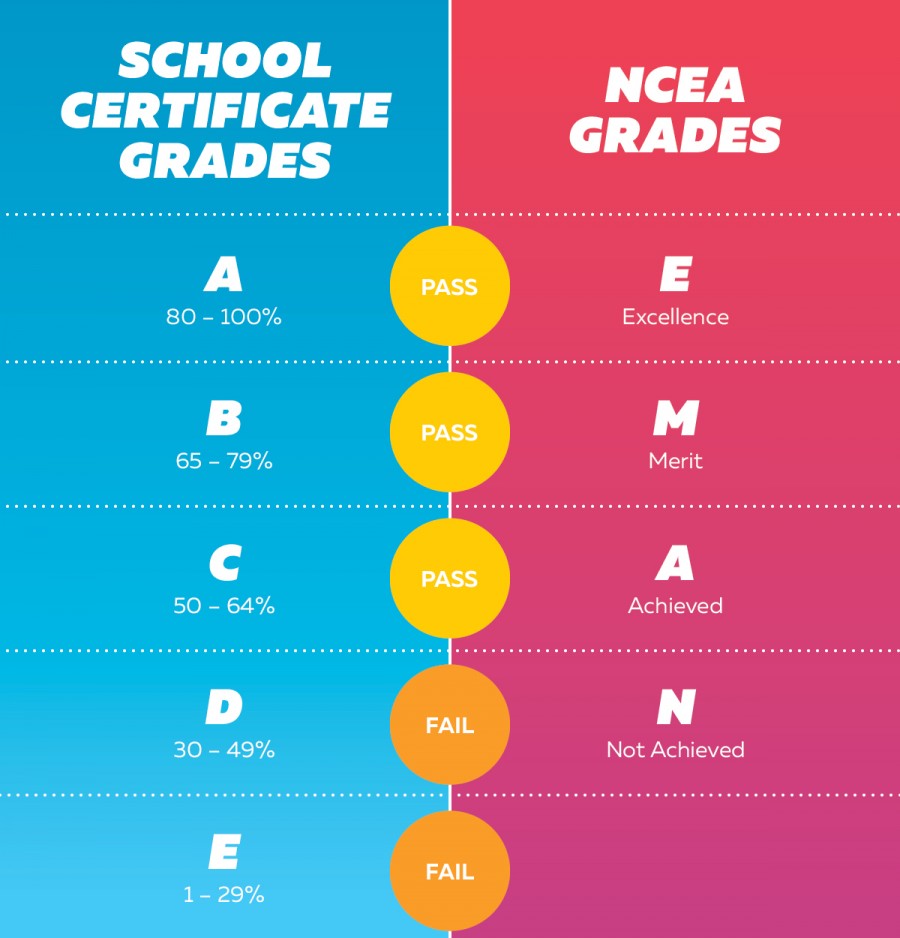
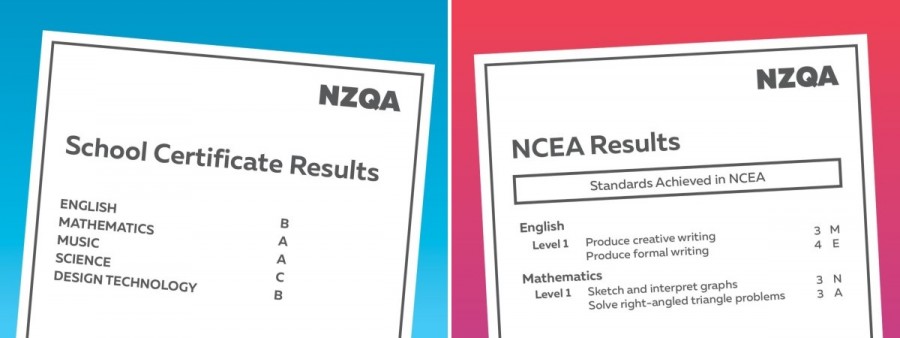
School Certificate and Bursary subjects were graded from A (for the highest scores) to E (for the lowest scores). Students passed a subject if they sat a three-hour exam and earned a C grade or higher.
NCEA subjects are made up of achievement standards and unit standards. Achievement standards are graded with N (not achieved), A (achieved), M (merit), or E (excellence). Unit standards are usually assessed as either A for achieved (pass) or N for not achieved (not passed).
How to earn an NCEA level certificate
Each NCEA standard is worth a number of credits. Students aim to earn enough credits across all their subjects to achieve an NCEA Level 1, 2 or 3 certificate.
Receiving results – then and now
- School Certificate and Bursary results were mailed to students in January.
- NCEA students can keep track of their internal assessment results online throughout the year by checking their record of achievement on the NZQA website. The official external examination results are posted online in January.
University Entrance – then and now
- Bursary students who passed three exams with at least a C grade earned University Entrance
- NCEA students who pass Level 3 with approved subjects and standards for University Entrance (UE) will automatically have UE appear on their online record of achievement.
University Entrance is NCEA Level 3 with:
- 14 credits each in three approved subjects
- 10 literacy credits (Level 2 or above)
- 10 numeracy credits (Level 1 or above).
Scholarship exams – then and now
- Scholarships and A and B Bursaries used to be awarded based on Bursary exam results.
- New Zealand Scholarship exams are usually studied in Year 13, but are not part of NCEA. New Zealand Scholarship is a financial reward for top-performing students who intend to enter tertiary study. The scholarship results don’t contribute towards a qualification.
Updated 14 Jun 2022