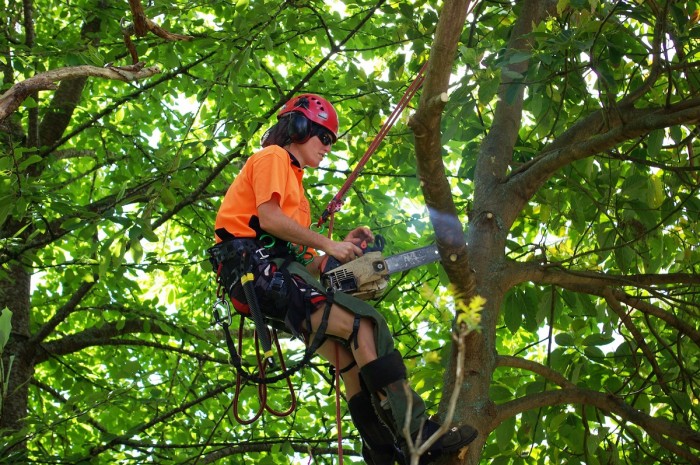
Arborist
Kaitiaki Rākau
Alternative titles for this job
Arborists plant and remove trees, prune branches and treat disease.
Pay
Arborists with up to five years' experience usually earn
$24-$25 per hour
Arborists with more than five years' experience usually earn
$25-$35 per hour
Source: New Zealand Arboricultural Association, 2021, Hamilton City Council, 2018.
Job opportunities
Pay
Pay for arborists varies depending on their experience and skills.
- New arborists usually start on the minimum wage.
- Arborists with one to four years' experience usually earn between minimum wage and $25 an hour.
- Arborists with more than five years' experience can earn between $25 and $35 an hour.
Self-employed arborists may earn more than this.
Source: New Zealand Arboricultural Association, 2021; and Hamilton City Council, 2018.
- PAYE.net.nz website – use this calculator to convert pay and salary information
- Employment New Zealand website - information about minimum wage rates
(This information is a guide only. Find out more about the sources of our pay information)
What you will do
Arborists may do some or all of the following:
- identify, inspect, maintain, prune, plant and move trees
- identify and remove hazards created by trees
- assess trees for potential risks
- use and maintain abseiling equipment to climb trees
- operate EWPs (elevated work platforms), chippers, chainsaws and trucks
- give advice on trees suitable for planting or removal, and tree care
- give advice on treatments for pests and diseases
- plan and carry out pest and disease management.
Utility arborists will also clear trees and vegetation from around powerlines.
Skills and knowledge
Arborists need to have knowledge of:
- plant and soil biology, tree species identification and pest and disease control
- tree planting, pruning and landscaping techniques
- tree climbing and tree removal techniques
- operating chainsaws, rigging and climbing equipment, EWPs and chippers
- safe work practices and first aid.
Working conditions
Arborists:
- may work nights and weekends and on call
- work outside on private properties, roadsides, parks and farms
- may work in hazardous conditions in bad weather and at heights.
What's the job really like?
Arborist video
Ryan Robinson talks about life as an arborist – 2. 23 mins
and it's stuck. Um, damn it. Hey,
my name's Ryan and I'm an arborist.
An arborist is a tree maintainer and remover.
So we prune and remove trees and we will do canopy
inspections to see if they're safe. Anything from the life till death of a tree.
We do remove and we do plant. Today we're just removing 2 pines.This one
on the right and then the one on the left with the ropes in it.
They are within falling distance of the house.
So preventative work. My favorite thing about my job is the variety and the fact
that every tree's different. Its surroundings are different.
So there's always the puzzle part of it. You get to work out your plan,
figure out how you're going to do it. There's a lot of room for creativity there.
You're able to come up with cool rope systems or cool plans to make your life
easier.
Gym muscles mean absolutely nothing as an arborist because the movements that we
do are so specific to our job. Yes,
you do need qualifications to be an arborist.
through an apprenticeship,
through an approved company. Mine took about a year.
A unique thing about being an
arborist is that a lot of people enjoy it so much that they do it outside of
work. They're actually tree climbing competitions all around the world.
Last year at the Auckland Comp [competition] , I came first.
Then now that's got me going to Singapore.
So it's also something that can help you travel and see the world. You
definitely need to have a good work ethic.
If you want to be an arborist that's very, very hard on your body.
But after a few years you'll build up the endurance and the skillset to be able
to climb all day long.
You can totally be afraid of heights if you want to be an arborist.
You've just got to slowly push your boundaries. When I first started,
I definitely wouldn't be comfortable up the tree this high.
I just really loved trees.
Growing up as a kid I was always free climbing and just doing stuff that kids
do. And then one day I saw an arborist climbing and I thought it was the coolest
thing. I got into it and found I love it and now it's my passion.
It's really important that we take care of our trees because they take care of us.
Entry requirements
To become an arborist you need to complete one of:
- a New Zealand Certificate in Horticulture Services (Level 4) with a strand in aboriculture
- an apprenticeship to gain a New Zealand Certificate in Primary Industry Skills (Horticulture)(Arboriculture)(Level 4).
- Otago Polytechnic website – arborist qualifications
- Waikato Institute of Technology website – arborist qualifications
- Primary Industry Training Organisation – arborist training and apprenticeships
- More information about apprenticeships
You need to have a full driver's licence and pass drug and alcohol tests.
A Class 2 truck licence and a First Aid Certificate are useful.
Secondary education
A minimum of three years of secondary education is recommended. Useful subjects include agriculture and horticulture, and biology.
Year 11 and 12 students can learn more about the horticulture industry, and study towards a National Certificate in Agriculture or Horticulture (Level 1 or 2), with a Trades Academy.
Year 12 and 13 students can learn more about the horticulture industry, and gain NCEA unit standards, through the Primary ITO Gateway programme.
Personal requirements
Arborists need to be:
- practical
- able to follow and give clear instructions
- able to keep calm in risky situations
- good at communicating with a wide range of people
- alert and observant, with an eye for detail
- safety conscious and responsible
- good at planning and organising.
Useful experience
Useful experience for arborists includes:
- horticulture or gardening work
- climbing with ropes
- customer service
- working at heights.
Physical requirements
Arborists need to have excellent fitness and must be strong to lift trees and branches. Arborists must be comfortable working at heights.
They should also have good balance, hand-eye co-ordination, hearing and eyesight (with or without corrective lenses).
Find out more about training
- New Zealand Arboricultural Association
- (04) 472 6330 - info@nzarb.org.nz - www.nzarb.org.nz
- Primary Industry Training Organisation
- 0800 208 020 - info@primaryito.ac.nz - www.primaryito.ac.nz
What are the chances of getting a job?
Demand for arborists strong
Demand for arborists is strong due to high demand for their services, and a shortage of trainees.
As a result, arborist appears on Immigration New Zealand's regional skill shortage list. This means the Government is actively encouraging skilled arborists from overseas to work in New Zealand.
According to the Census, 1614 arborists worked in New Zealand in 2018.
Types of employers varied
Arborists may work for:
- city and regional councils
- arborist companies
- power companies.
Sources
- Chapman, M, 'Partnership Key to Address Labour Shortages', 13 April 2018, (www.hortnz.co.nz).
- Chapman, M, 'Where are the Workers?', 16 March 2018, (www.hortnz.co.nz).
- Fiske, Z, arborist, Hamilton City Council, careers.govt.nz interview, May 2018.
- Immigration New Zealand, 'Regional Skill Shortage List', 27 May 2019, (www.immigration.govt.nz).
- Lines-Mackenzie, J, 'One of the World's Best Tree Climbers Wants some More Competition', 11 April 2-17, (www.stuff.co.nz).
- Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment, 'Jobs Online Monthly report - April 2018', 15 May 2018, (www.mbie.govt.nz).
- Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment, 'Jobs Online Quarterly report - March 2018', 27 April 2018, (www.mbie.govt.nz).
- Molloy, K, business partner people and capability, Napier City Council, careers.govt.nz interview, June 2018.
- New Zealand Arborists Association, 'Tree Matters Winter 17', (www.nzarb.org.nz).
- Otago Polytechnic website, accessed May 2018, (www.op.ac.nz).
- Penman, C, '"Wholesale Slaughter" of Auckland Trees', 13 October 2017, (www.nzherald.co.nz).
- Stats NZ, '2018 Census Data', 2019.
- Wilson, W, human resources manager, Palmerston North City Council, careers.govt.nz interview, June 2018.
(This information is a guide only. Find out more about the sources of our job opportunities information)
Progression and specialisations
Arborists may progress to set up their own arboriculture business, or move into supervisory or management roles.
Arborists may also progress to become consultants on tree disease and risk management, or on planning trees for public spaces.
Arborists may specialise in:
- climbing – using equipment to climb and prune trees
- diagnostics – identifying and treating tree diseases
- EWP operation – using an elevated work platform to prune trees
- utility arboriculture – pruning and clearing trees near power lines or cables.
Last updated 9 May 2025